We have covered the evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) over the years as they have gained prominence. IoT devices collect a massive amount of data. Cisco projects by the end of 2021, IoT devices will collect over 800 zettabytes of data per year. Meanwhile, AI algorithms can parse through big data and teach themselves to analyze and identify patterns to make predictions. Both technologies enable a seemingly endless amount of applications retained a massive impact on many industry verticals.
What happens when you merge them? The result is aptly named the AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) and it will take IoT devices to the next level.
WHAT IS AIOT?
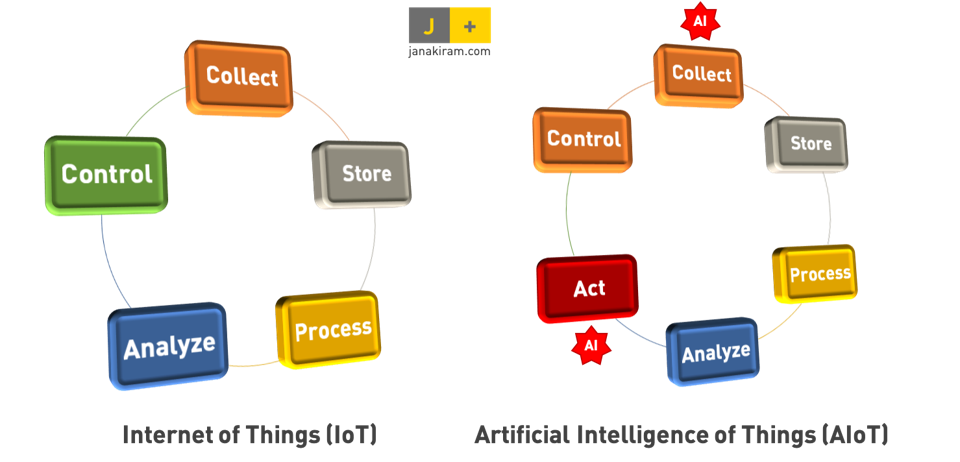
AIoT is any system that integrates AI technologies with IoT infrastructure, enhancing efficiency, human-machine interactions, data management and analytics.
IoT enables devices to collect, store, and analyze big data. Device operators and field engineers typically control devices. AI enhances IoT’s existing systems, enabling them to take the next step to determine and take the appropriate action based on the analysis of the data.
By embedding AI into infrastructure components, including programs, chipsets, and edge computing, AIoT enables intelligent, connected systems to learn, self-correct and self-diagnose potential issues.
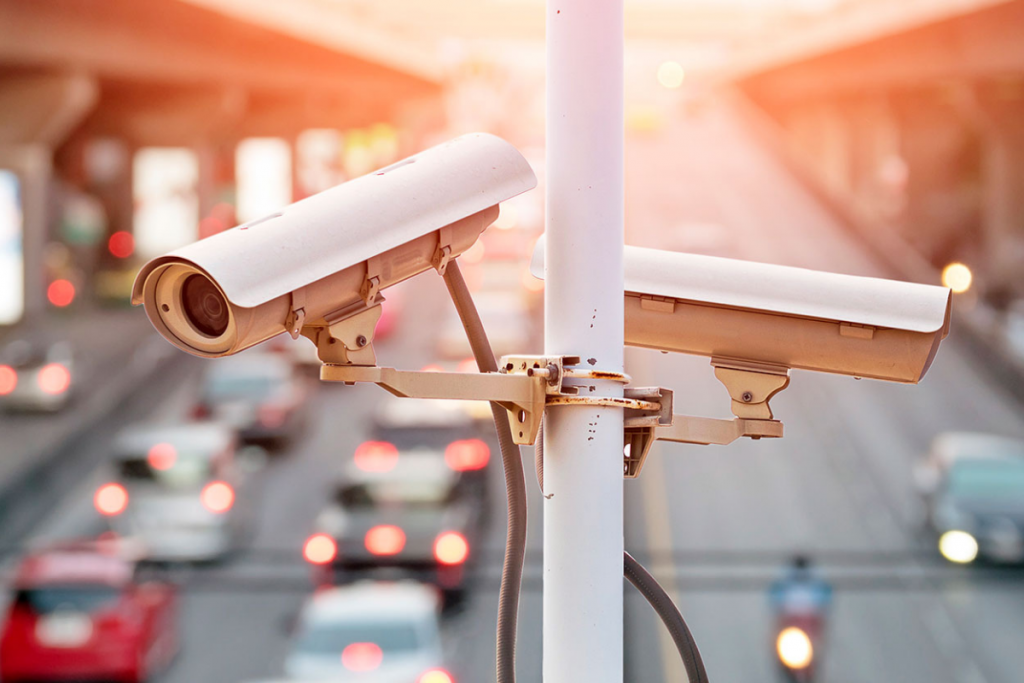
One common example comes in the surveillance field. Surveillance camera can be used as an image sensor, sending every frame to an IoT system which analyzes the feed for certain objects. AI can analyze the frame and only send frames when it detects a specific object—significantly speeding up the process while reducing the amount of data generated since irrelevant frames are excluded.
While AIoT will no doubt find a variety of applications across industries, the three segments we expect to see the most impact on are wearables, smart cities, and retail.
WEARABLES
The global wearable device market is estimated to hit more than $87 billion by 2022. AI applications on wearable devices such as smartwatches pose a number of potential applications, particularly in the healthtech sector.
Researchers in Taiwan have been studying the potential for an AIoT wearable system for electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis and cardiac disease detection. The system would integrate a wearable IoT-based system with an AI platform for cardiac disease detection. The wearable collects real-time health data and stores it in a cloud where an AI algorithm detects disease with an average of 94% accuracy. Currently, Apple Watch Series 4 or later includes an ECG app which captures symptoms of irregular, rapid or skipped heartbeats.
Although this device is still in development, we expect to see more coming out of the wearables segment as 5G enables more robust cloud-based processing power, taking the pressure off the devices themselves.
SMART CITIES
We’ve previously explored the future of smart cities in our blog series A Smarter World. With cities eager to invest in improving public safety, transport, and energy efficiency, AIoT will drive innovation in the smart city space.
There are a number of potential applications for AIoT in smart cities. AIoT’s ability to analyze data and act opens up a number of possibilities for optimizing energy consumption for IoT systems. Smart streetlights and energy grids can analyze data to reduce wasted energy without inconveniencing citizens.
Some smart cities have already adopted AIoT applications in the transportation space. New Delhi, which boasts some of the worst traffic in the world, features an Intelligent Transport Management System (ITMS) which makes real-time dynamic decisions on traffic flows to accelerate traffic.
RETAIL
AIoT has the potential to enhance the retail shopping experience with digital augmentation. The same smart cameras we referenced earlier are being used to detect shoplifters. Walmart recently confirmed it has installed smart security cameras in over 1,000 stores.
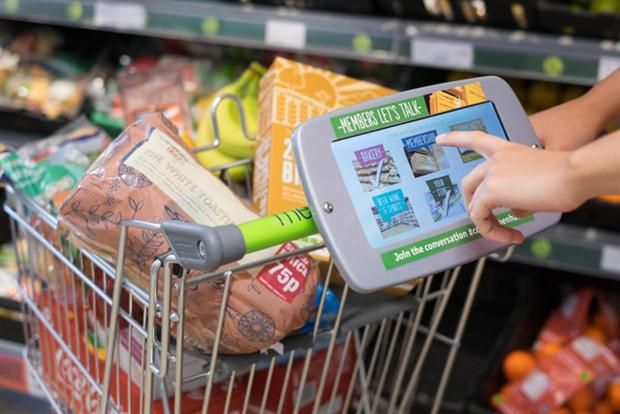
One of the big innovations for AIoT involves smart shopping carts. Grocery stores in both Canada and the United States are experimenting with high-tech shopping carts, including one from Caper which uses image recognition and built-in sensors to determine what a person puts into the shopping cart.
The potential for smart shopping carts is vast—these carts will be able to inform customers of deals and promotion, recommend products based on their buying decisions, enable them to view an itemized list of their current purchases, and incorporate indoor navigation to lead them to their desired items.
A smart shopping cart company called IMAGR recently raised $14 million in a pre-Series A funding round, pointing toward a bright future for smart shopping carts.
CONCLUSION
AIoT represents the intersection of AI, IoT, 5G, and big data. 5G enables the cloud processing power for IoT devices to employ AI algorithms to analyze big data to determine and enact action items. These technologies are all relatively young, and as they continue to grow, they will empower innovators to build a smarter future for our world.