The Internet of Behaviors (IoB) is transforming how we interact with technology and data. By leveraging insights from user behaviors, IoB aims to enhance user experiences, streamline operations, and drive innovation across various sectors. Among its most promising applications is within the realm of smart cities. IoB smart cities are designed to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable urban environments by integrating IoT devices, data analytics, and behavioral insights. In this blog, we’ll delve into what makes IoB smart cities a blueprint for the future.
The Rise of Smart Cities
The concept of smart cities revolves around creating environments that are not only technologically advanced but also focused on improving the everyday experiences of their inhabitants. At the core, smart cities utilize a network of interconnected devices and systems—often referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT) —to gather real-time data. This extensive data collection enables city planners and administrators to make informed decisions on urban planning and management.
For instance, smart transportation systems can reduce traffic congestion and improve public transit efficiency by analyzing patterns and predicting travel demands. Similarly, smart grids help optimize energy consumption, leading to more sustainable power usage and reduced environmental impact. Waste management systems benefit from sensors that monitor bin levels and dynamically adjust collection routes, ensuring efficient resource use and cleaner urban spaces. Public services such as street lighting, emergency response, and even healthcare are enhanced through data-driven approaches that adapt to the needs of residents.
Overall, the vision of a smart city is to seamlessly integrate technology and data into the urban fabric, creating a responsive, adaptive, and holistic environment that prioritizes the well-being of its citizens while managing resources judiciously.
The Importance of IoB Smart Cities
The importance of IoB smart cities cannot be overstated. They represent a critical step towards creating urban environments that are not only more efficient and sustainable but also more responsive to the needs and behaviors of their inhabitants. By harnessing the power of data, IoB smart cities can optimize resource allocation, enhance public services, and foster economic growth, ultimately improving the quality of life for their residents. As we continue to explore the potential of IoB, smart cities will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping our future. So, it is crucial to monitor and regulate their development carefully. IoB smart cities can pave the way toward a smarter, more connected, and sustainable future with proper planning and consideration for ethical and privacy concerns.
As we continue to innovate and expand our understanding of IoB, the potential for smart cities will only continue to grow. By embracing the principles of sustainability, efficiency, and citizen-centric design, IoB smart cities have the power to create a better world for all. With careful planning and consideration for ethical and privacy concerns, these cities can pave the way toward a smarter, more connected, and sustainable future.
Benefits of IoB Smart Cities
One of the primary advantages of IoB smart cities is their contribution to sustainability and the environment. Utilizing green energy solutions such as solar panels and wind turbines, these cities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Additionally, advanced waste management systems powered by IoB technologies enable efficient sorting and recycling processes, leading to reduced landfill usage. Air quality monitoring devices provide real-time data, helping to mitigate pollution and protect public health. Water conservation efforts are also enhanced through smart metering and leak detection technologies, ensuring sustainable water usage. Overall, IoB smart cities promote sustainable living and contribute to a healthier environment.
Urban Mobility
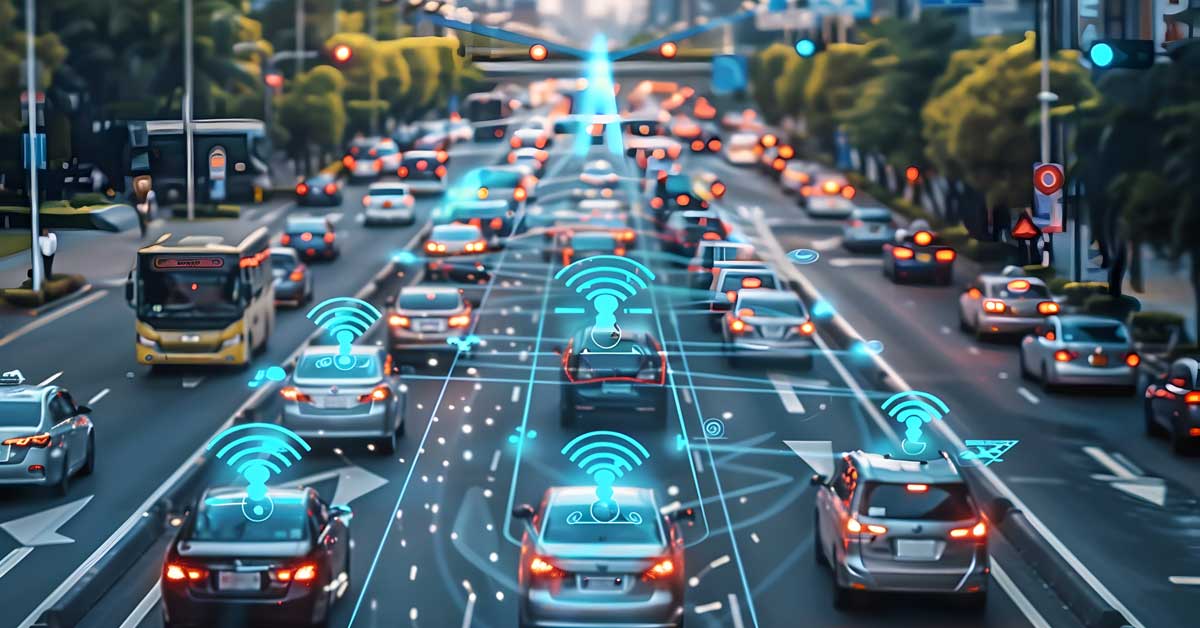

Urban mobility is another area where IoB smart cities excel. Autonomous vehicles, guided by IoB data, promise to reduce traffic congestion and lower accident rates, offering a safer and more efficient mode of transport. Innovations in public transport include real-time scheduling and route optimization based on passenger behavior and preferences. Bike-sharing programs, powered by IoB, provide a flexible and eco-friendly alternative to traditional transportation methods. Advanced traffic management systems use data analytics to adjust traffic signals dynamically, reducing wait times and improving overall traffic flow. These advancements contribute to a more streamlined and efficient urban mobility experience.
Public Safety and Security

Public safety and security are paramount in IoB smart cities. Modern surveillance systems equipped with facial recognition and behavior analysis can preemptively identify and address potential security threats. Emergency response technologies, such as connected fire alarms and medical alert systems, ensure rapid assistance during crises. Cybersecurity measures are crucial to protect the vast amounts of data generated and stored within IoB ecosystems, safeguarding both infrastructure and citizen information from malicious attacks. Through these technological advancements, IoB smart cities create a safer and more secure environment for their citizens.
Healthcare
In terms of healthcare and well-being, IoB plays a transformative role. Telemedicine services allow for remote consultations, making healthcare more accessible, especially in underserved areas. Smart hospitals utilize IoB technologies for patient monitoring, resource management, and operational efficiency, improving the overall standard of care. Wearable health monitoring systems enable individuals to track their vital signs and receive personalized health advice. Public health data collected through IoB devices aid in the early detection and management of disease outbreaks, promoting a healthier community. These advancements in healthcare and well-being, powered by IoB, contribute to a better quality of life for citizens.
Smart Governance

Smart governance is another cornerstone of IoB smart cities. E-governance platforms facilitate seamless interaction between citizens and government bodies, improving service delivery and citizen satisfaction. Data-driven decision-making ensures that policies and initiatives are based on accurate and timely information, enhancing their efficacy. Citizen services, such as online portals for utilities and permits, simplify processes and reduce administrative burdens. Open data initiatives enable citizens to access and analyze government data, fostering transparency and accountability. Through these digital advancements, IoB smart cities promote efficient, transparent, and responsive governance.
Connectivity in IoB Communities

Communities within IoB smart cities are connected through a seamless network of IoT devices and data platforms. This interconnectedness enables real-time communication and collaboration across various sectors. For example, smart grids dynamically balance energy supply and demand, while smart street lighting adjusts based on pedestrian and vehicular traffic patterns. Public transport systems communicate with traffic management centers to optimize routes and schedules, ensuring efficient and reliable service. These connected communities also foster citizen engagement and participation through social media platforms and community forums, allowing for input and feedback on various initiatives. The connectivity in IoB communities promotes a sense of belonging and enables collaboration towards shared goals, ultimately creating a more cohesive society.
Furthermore, IoB technologies facilitate community engagement. Residents can provide feedback and report issues through mobile apps, contributing to continuous improvement and fostering a sense of ownership and participation. Social media platforms and online forums enable the sharing of experiences and ideas, strengthening community bonds.
Cons of IoB Smart Cities
Despite their numerous benefits, IoB smart cities have challenges. The reliance on extensive data collection raises significant privacy concerns. Ensuring that personal information is securely stored and ethically used is paramount to maintaining public trust. Additionally, the high cost of implementation and maintenance can be a barrier for some municipalities. Integrating diverse technologies requires substantial investment in infrastructure and ongoing operational costs.
There is also the risk of technological obsolescence. As new technologies emerge, existing systems may become outdated quickly, necessitating continuous upgrades and investments. Interoperability issues arise when integrating multiple IoT devices and platforms, potentially leading to inefficiencies and increased complexity. Finally, the need for standardization and regulations for IoB technologies can create compliance challenges and hinder widespread adoption. Policymakers and industry leaders need to address these concerns and establish guidelines to ensure the responsible implementation of IoB in smart cities.
The Future of IoB Smart Cities

Looking ahead, the potential of IoB smart cities is immense. Future developments may include even more sophisticated AI and machine learning algorithms capable of predicting and responding to urban challenges with unprecedented accuracy. Enhanced connectivity through 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable communication between devices, enabling more complex and integrated solutions. As the IoB ecosystem continues to expand, it will also create new job opportunities in fields such as data science and cyber security. However, careful consideration must be given to data privacy and security as these technologies continue to evolve. As technology continues to shape the world around us, IoB smart cities will play a crucial role in how we design and manage our urban environments. By leveraging the power of data, connectivity, and citizen engagement, these cities have the potential to become more sustainable, efficient, and responsive
We can also expect advancements in autonomous systems, from self-driving cars to drone-based delivery services, further revolutionizing urban mobility and logistics. The integration of virtual and augmented reality technologies may offer new ways for citizens to interact with their environment, from virtual city tours to augmented reality navigation aids. The possibilities are endless, and as we continue to push the boundaries of what is possible with IoB, smart cities will continue to evolve and shape the world around us. Municipalities, policymakers, and industry leaders need to work together to ensure the responsible and ethical development of IoB smart cities for the betterment of society as a whole. With careful planning, collaboration, and consideration for all stakeholders, we can create a future where technology enhances our lives and makes our cities smarter, more connected, and more sustainable than ever before.
Conclusion
IoB smart cities represent a promising vision for the future of urban living. By integrating IoT devices, data analytics, and behavioral insights, these cities can achieve greater efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life for their residents. However, addressing privacy, cost, and technological obsolescence challenges is crucial for realizing their full potential.
As we continue to explore the possibilities of IoB, the next frontier lies in its application to behavioral analysis, which will be the focus of our upcoming blog. In our next blog, we will dive deeper into how IoB revolutionizes behavioral analysis, offering new insights into human behavior and driving innovations across various sectors.