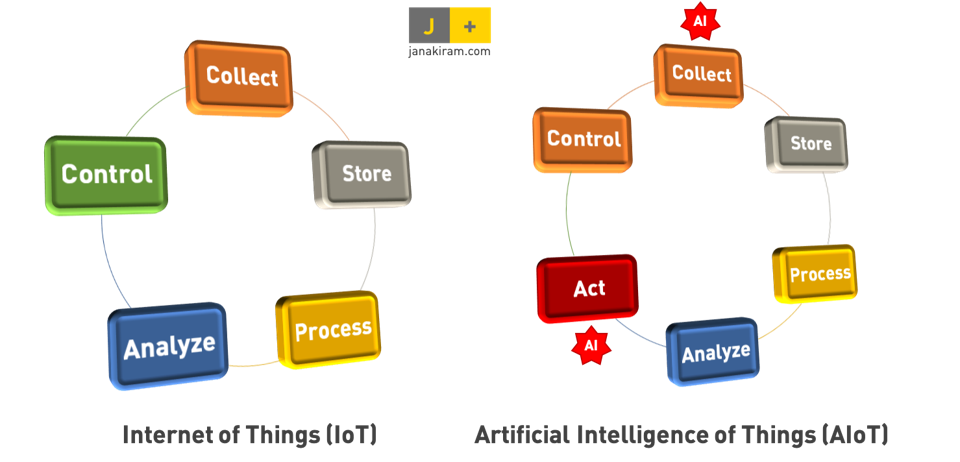
Throughout this blog series on Edge AI, we have touched upon various fascinating applications, including Edge AI in autonomous vehicles and Edge AI in consumer electronics. In autonomous vehicles, edge AI plays a pivotal role in enabling real-time decision-making and improving the overall safety and efficiency of transportation systems. Meanwhile, in consumer electronics, edge AI enhances user experiences by providing smart, responsive features in everyday devices such as smartphones, smart home systems, and wearable technology.
Lastly, in the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, Edge AI is paving new ways to harness the power of IoT (Internet of Things) devices and smart sensors. These advancements are not just buzzwords but fundamental shifts that promise to enhance efficiency, improve data management, and offer unprecedented insights. This blog will explore the effects of Edge AI on IoT devices and smart sensors, providing insights into its current applications, benefits, and future potential. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how Edge AI can revolutionize your business operations.
Smart Sensors Explained
This RealPars video explores the transformative role of Smart Sensors in Industry 4.0’s Smart Factory framework
The Intersection of Edge AI and IoT

Enhancing Real-Time Data Processing
One of the most significant benefits of Edge AI is its ability to process data in real-time. Traditional IoT systems often rely on cloud-based servers to analyze data, which can result in delays and increased latency. Edge AI mitigates these issues by enabling IoT devices to process and analyze data locally. This real-time processing capability is crucial for applications requiring immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation.
For example, consider a manufacturing plant equipped with smart sensors to monitor machinery performance. With Edge AI, any anomalies in the data can be detected and addressed instantly, preventing potential breakdowns and costly downtime.
Improving Bandwidth Efficiency
Bandwidth efficiency is another critical advantage of Edge AI on IoT devices. Sending vast amounts of raw data to the cloud for processing can strain network resources and incur significant costs. By processing data locally, Edge AI reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted, thus optimizing bandwidth usage.
Imagine a smart city project where thousands of sensors collect data on traffic, weather, and public safety. Edge AI can filter and preprocess this data locally, sending only the most relevant information to the central server. This approach not only conserves bandwidth but also ensures faster and more efficient decision-making.
Enhancing Security and Privacy

Security and privacy are paramount concerns in the age of data-driven technologies. Edge AI offers enhanced security by minimizing the need to transfer sensitive data over the network. Localized data processing reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, making it a more secure option for businesses dealing with sensitive information.
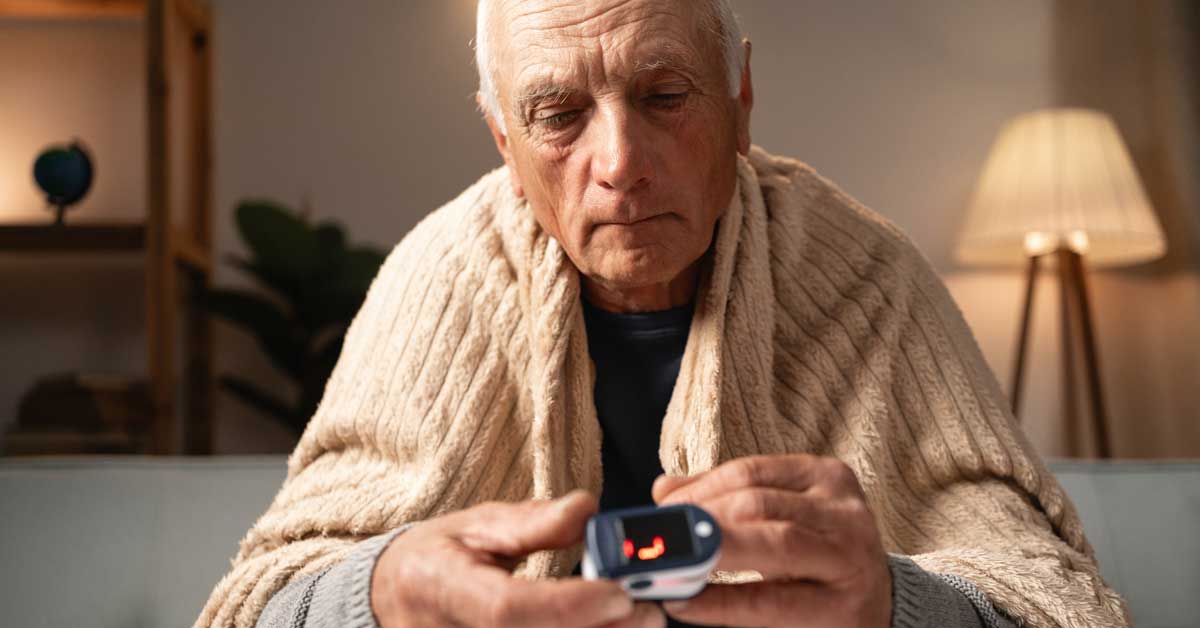
For instance, healthcare facilities using IoT devices to monitor patient vitals can benefit from Edge AI. By processing data locally, patient information remains within the facility’s secure network, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Take, for example, a hospital equipped with smart beds that monitor patient heart rates, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. With Edge AI, these smart beds can analyze data in real-time and alert medical staff to any abnormalities immediately, thereby enhancing patient care and response times.
Another example is remote patient monitoring systems used in home healthcare setups. Edge AI can process data from wearable devices, such as glucose monitors or digital stethoscopes, ensuring that sensitive health information is analyzed on the device itself before only the necessary summarized data is sent to healthcare providers. This not only preserves the patient’s privacy but also ensures timely intervention when needed.
Pros of Edge AI on IoT Devices and Smart Sensors
Reduced Latency
One of the most significant advantages of Edge AI is its ability to reduce latency. By processing data closer to the source, Edge AI eliminates the delays associated with transmitting data to and from cloud servers. This reduced latency is crucial for applications requiring real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles or industrial automation.
Consider a smart factory where machines are equipped with sensors to monitor their performance. With Edge AI, any anomalies in the data can be detected and addressed instantly, preventing potential breakdowns and costly downtime.
In an automated warehouse where robotic systems manage inventory, Edge AI can be used to process data from various sensors in real time. If a sensor detects an obstruction in the robot’s path, Edge AI can immediately reroute the robot, avoiding potential collisions and maintaining a smooth flow of operations. This instant decision-making capability minimizes interruptions and maximizes operational efficiency, showcasing how Edge AI significantly benefits environments that rely on the timely processing of critical data.
Improved Bandwidth Efficiency
Another positive aspect of Edge AI is its ability to enhance bandwidth efficiency. By processing data locally, Edge AI minimizes the volume of data transmitted to central servers. This is particularly advantageous for data-intensive applications, such as video surveillance or smart city monitoring. For instance, in a smart city, Edge AI can process video feeds from traffic cameras locally and only send relevant alerts or summarized data, significantly reducing network load and transmission costs.
Enhanced Resilience and Reliability
Edge AI enhances system resilience and reliability by ensuring critical functions can operate even without network connectivity. For instance, in autonomous vehicles, edge computing allows real-time decision-making even in regions with poor internet connections. Similarly, in industrial automation, machines can perform essential operations independently of cloud-based systems. This decentralized approach ensures that even in the event of network failures, Edge AI devices maintain functionality and consistent performance.
Cons of Edge AI on IoT Devices and Smart Sensors

Initial Setup Costs
One of the primary challenges of implementing Edge AI is the initial setup cost. Deploying Edge AI infrastructure requires significant investment in hardware, software, and skilled personnel. For small and medium-sized businesses, these costs can be a barrier to adoption.
However, it’s important to consider the long-term benefits and potential cost savings associated with Edge AI. Businesses that invest in Edge AI can achieve significant returns through improved efficiency, reduced operational costs, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Limited Processing Power
Another potential drawback of Edge AI is the limited processing power of edge devices. Unlike cloud servers, edge devices may have limited computational resources, which can impact their ability to handle complex AI algorithms.
Businesses must carefully evaluate their specific use cases and determine whether Edge AI devices have the necessary processing power to meet their needs. In some cases, a hybrid approach that combines edge and cloud processing may be the most effective solution.
Data Management Challenges

Edge AI also presents data management challenges for businesses. With data being processed and stored on various edge devices, managing and maintaining this data can be complex and time-consuming. This issue is further compounded by the sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices, making it challenging to extract meaningful insights.
To address this challenge, businesses must have robust data management strategies in place, including implementing efficient data storage solutions and leveraging advanced analytics tools to make sense of large datasets. Overall, while there are challenges associated with Edge AI on IoT devices, its numerous benefits make it a valuable tool for businesses looking to utilize real processing and improve decision-making capabilities.
Maintenance and Management
Maintaining and managing Edge AI infrastructure can be challenging, especially for businesses with limited IT resources. Edge devices require regular updates, monitoring, and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and security. Businesses can partner with managed service providers (MSPs) that specialize in Edge AI deployment and management. MSPs can provide the expertise and support needed to maintain a robust and secure Edge AI infrastructure.
Future Plans and Developments

Advancements in Edge AI Hardware
The future of Edge AI is bright, with ongoing advancements in hardware technology. Next-generation edge devices will feature more powerful processors, enhanced memory capabilities, and improved energy efficiency. These advancements will enable businesses to deploy even more sophisticated AI algorithms at the edge.
For example, companies like NVIDIA and Intel are developing cutting-edge processors specifically designed for Edge AI applications. These processors will enable faster and more efficient data processing, opening up new possibilities for IoT and smart sensor applications.
Integration with 5G Networks

The rollout of 5G networks will significantly impact the adoption of Edge AI. With its ultra-low latency and high-speed data transmission capabilities, 5G will enhance the performance of Edge AI applications, enabling real-time decision-making and data processing on a larger scale.
Industries such as autonomous driving, smart cities, and industrial automation will benefit greatly from the combination of 5G and Edge AI. The synergy between these technologies will drive innovation and transform the way businesses operate. Overall, the future of Edge AI looks promising, with endless possibilities for improving efficiency, security, and decision-making capabilities in various industries. As hardware technology continues to advance and more businesses adopt Edge AI solutions, we can expect to see even greater developments and advancements in this field.
Expansion of Edge AI Use Cases
As Edge AI technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see an expansion of use cases across various industries. From healthcare and agriculture to manufacturing and retail, businesses will find new and innovative ways to leverage Edge AI to improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and drive growth.
For instance, in agriculture, Edge AI-powered drones can monitor crop health in real time, enabling farmers to make data-driven decisions and optimize their yields. In retail, smart shelves equipped with Edge AI can track inventory levels and automatically reorder products, reducing stock outs and improving customer satisfaction. The possibilities are endless, and the future of Edge AI is full of exciting potential. One example of a company that is in charge of creating Edge AI-powered drones for agriculture is DroneDeploy. DroneDeploy offers innovative solutions that enable farmers to monitor crop health with precision and efficiency.
Conclusion
As we conclude our Edge AI blog series, we hope you have gained valuable insights into the benefits, challenges, and future developments associated with this transformative technology. From understanding its impact on various industries to exploring its innovation potential, Edge AI represents a significant advancement in the way we process and utilize data.
Edge AI is revolutionizing the way businesses leverage IoT devices and smart sensors. By enabling real-time data processing, optimizing bandwidth usage, and enhancing security, Edge AI offers significant benefits for businesses across various industries. However, it’s essential to consider the initial setup costs, limited processing power, and maintenance challenges associated with Edge AI.
Looking ahead, advancements in Edge AI hardware, integration with 5G networks, and the expansion of use cases will drive the continued growth and adoption of this technology. For CEOs, technology executives, and business owners, staying informed about Edge AI developments and exploring its potential applications can provide a competitive advantage in today’s tech-driven world. Stay tuned for more in-depth explorations of the latest trends and technologies shaping our world.