In the last installment of our blog series on smart cities, we examined how smart transportation will make for a more efficient society. This week, we’ll examine how urban security stands to evolve with the implementation of smart technology.
Smart security in the modern era is a controversial issue for informed citizens. Many science fiction stories have dramatized the evolution of technology, and how every advance increases the danger of reaching a totalitarian state—particularly when it comes to surveillance. However, as a society, it would be foolish to refrain from using the technical power afforded to us to protect our cities.
Here are the top applications for smart security in the smart cities of the future:
Surveillance
Surveillance has been a political point of contention and paranoia since the Watergate scandal in the early 1970s. Whistleblower Edward Snowden became a martyr or traitor depending on your point of view when he exposed vast surveillance powers used by the NSA. As technology has rapidly evolved, the potential for governments to abuse their technological power has evolved with it.
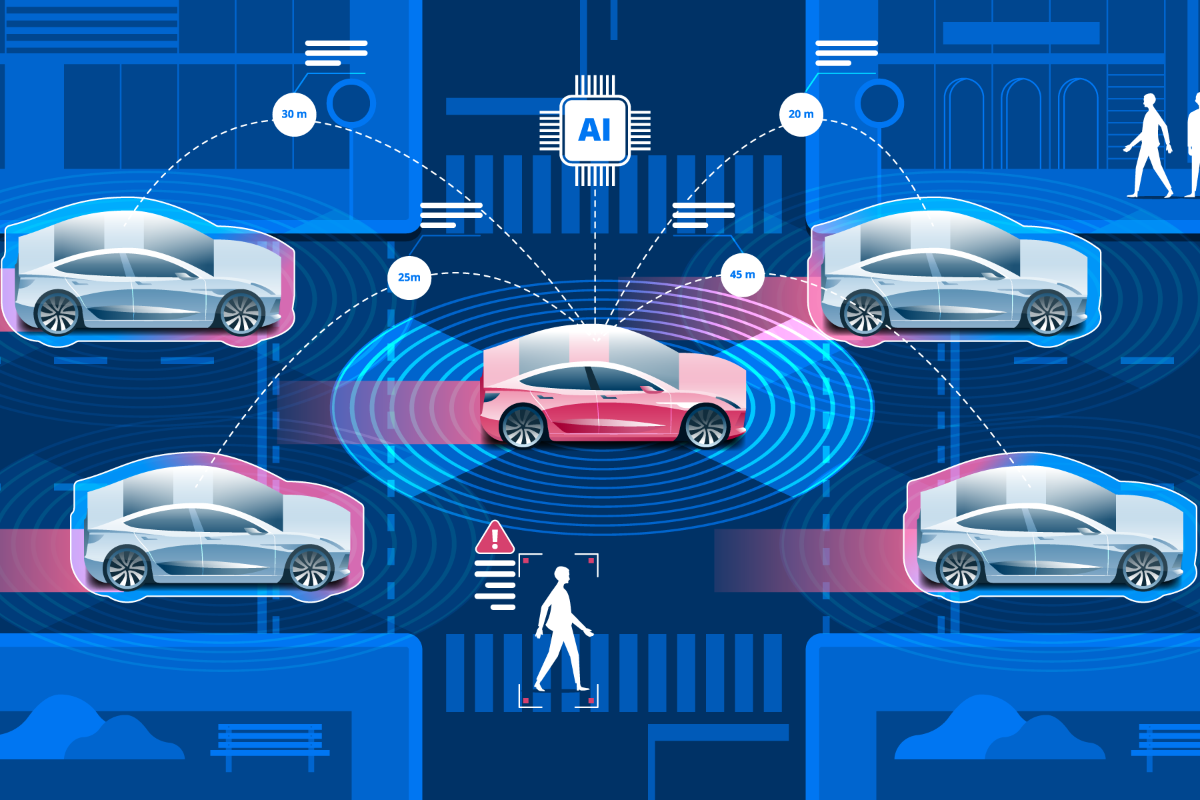
Camera technology has evolved to the point where everyone has a tiny camera on them at all time via their phones. While monitoring entire cities with surveillance feeds is feasible, the amount of manpower necessary to monitor the footage and act in a timely manner rendered this mass surveillance ineffective. However, deep learning-driven AI video analytics tools can analyze real-time footage and identify anomalies, such as foreboding indicators of violence, and notify nearby law enforcement instantly.
In China, police forces use smart devices allied to a private broadband network to discover crimes. Huawei’s eLTE system allows officers to swap incident details securely and coordinate responses between central command and local patrols. In Shanghai, sophisticated security systems have seen crime rates drop by 30% and the amount of time for police to arrive at crime scenes drop to 3 minutes.
In Boston, to curb gun violence, the Boston police force has deployed an IoT sensor-based gunfire detection system that notifies officers to crime scenes within seconds.
Disaster Prevention
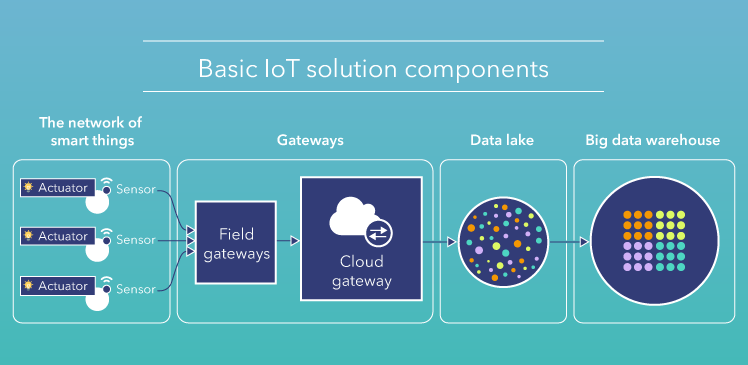
One of the major applications of IoT-based security system involves disaster prevention and effective use of smart communication and alert systems.
When disasters strike, governments require a streamlined method of coordinating strategy, accessing data, and managing a skilled workforce to enact the response. IoT devices and smart alert systems work together to sense impending disasters and give advance warning to the public about evacuations and security lockdown alerts.
Cybersecurity
The more smart applications present in city infrastructure, the more a city becomes susceptible to cyber attack. Unsecured devices, gateways, and networks each represent a potential vulnerability for a data breach. The average cost of a data breach according to IBM and the Poneman Institute is estimated at $3.86 million dollars. Thus, one of the major components of securing the smart city is the ramping up of cybersecurity to prevent hacking.
The Industrial Internet Consortium are helping establish frameworks across technologies to safely accelerate the Industrial Internet of Things (IIot) for transformational outcomes. GlobalSign works to move secure IoT deployments forward on a world-wide basis.
One of the first and most important steps toward cybersecurity is adopting standards and recommended guidelines to help address the smart city challenges of today. The Cybersecurity Framework is a voluntary framework consisting of standards, guidelines, and best practices to manage cybersecurity-related risk published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), a non-regulatory agency in the US Department of Commerce. Gartner projects that 50% of U.S. businesses, critical infrastructure operators, and countries around the globe will use the framework as they develop and deploy smart city technology.
Conclusion
The Smart City will yield a technological revolution, begetting a bevy of potential applications in different fields, and with every application comes potential for hacker exploitation. Deployment of new technologies will require not only data standardization, but new security standardizations to ensure that these vulnerabilities are protected from cybersecurity threats. However, don’t expect cybersecurity to slow the evolution of the smart city too much as it’s expected to grow into a $135 billion dollar industry by 2021 according to TechRepublic.
This concludes our blog series on Smart Cities, we hope you enjoyed and learned from it! In case you missed it, check out our past entries for a full picture of the future of smart cities:
A Smarter World Part 1: How the Future of Smart Cities Will Change the World
A Smarter World Part 2: How Smart Infrastructure Will Reshape Your City
A Smarter World Part 3: How Smart Transportation Will Accelerate Your Business