Web3 has become an increasingly popular buzzword in tech circles. While some are fervent believers in its potential to change the internet as we know it, others are skeptical it holds the future. Still others have no clue what it is—and rightfully so. Web3 entails a set of online principles with potentially mammoth ramifications, but one of the major questions surrounding it is how will these principles take hold? Web3 could manifest in a variety of ways.
This week, we delve into how it may change the internet as we know it.
WHAT IS WEB3?

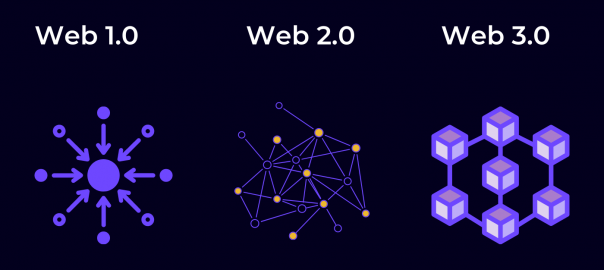
To answer this question, first we’ll explain the Web1 and Web2.
Web1 is the original version of the internet—think of it as a read-only version. In 1991, HTML and URLs allow users to navigate between static pages. After the millennium, the internet starts to become interactive. User-generated content gradually takes hold via MySpace and eventually Facebook, Twitter, and other social media platforms. This interactive version of the internet constitutes Web2, it’s a version of the internet in which users can both read and write via social media, Wikipedia, YouTube and more.
Tech conglomerates naturally turned Web2 into an era of centralization. Meta owns three of the four biggest social apps in the world. YouTube, the fourth biggest social network, is owned by Google, which accounts for around 90% of internet searches. Many question the ethics behind so much data in the hands of so few behemoths. Some have gone so far as to question whether the combination of big data and AI could diminish our capacity for free will, while other research shows that the targeted ad economy does not add much value and may in fact be a bubble.
In the face of these prescient concerns, the main thing that separates Web3 is the concept of decentralization.
DECENTRALIZED WEB
One of the main principles of Web3 is that it employs blockchain technology to decentralize data ownership and, in the words of Packy McCormick who helped popularize the term Web3, an “internet owned by the builders and users, orchestrated with tokens.”
The concept of digital decentralization gained massive traction since Satoshi Nakamoto created Bitcoin using the blockchain in 2009. Cryptocurrency has since become a household name and blockchain technology is finding adoption in a multitude of ways.
In Web3, centralized corporate platforms will be replaced with open protocols and community run networks, enabling the open infrastructure of Web1 with the user-participation of Web2. Everything is decentralized using the blockchain. Decentralization means that a distributed ledger manages financial transactions rather than a single server.
When going to a major social network like Instagram, rather than giving their data away for free, users could monetize their data and receive cryptocurrency for creating interesting posts. Users could buy stakes in up-and-coming artists to become patrons in exchange for a percentage of their royalties. Axie Infinity is a popular Web3 video game which uses NFTs and Ethereum to reward users for achieving in-game objectives. Games with real-life rewards are known as Play to Earn or “P2E” games—a major new trend in game design. It follows the overall goal of Web3—to put power in the hands of users and creators rather than major corporations.
CRYPTOCURRENCY AND NFTS

Blockchain technologies enable an economy powered by NFTs and cryptocurrency. Users can use cryptocurrencies like Ethereum to purchase NFT versions of real-life moments, memes, emojis and more. For example, NBA: Top Shot was among the first NFT projects from a major brand. Fans could purchase “moments” in NBA history, such as Jordan’s famous shot in Game 5 of the 1989 NBA playoffs first round, and trade them as if they were trading cards. It creates a community for fans using digital assets.
The digital art contained within NFTs can be copied but original ownership cannot be duplicated. It’s similar to owning an original Picasso—other people may have copies of the same art, but there is only one original.
Bored Ape Yacht Club may be the most successful NFT project—offering access to real-life parties and online spaces in exchange for purchasing their NFTs.
Another blockchain-powered phenomenon is Decentralized Autonomous Organizations or DAOs. DAOs are organizations that raise and spend money, but all decisions are voted on by members and executed using rules encoded in the blockchain. Famously, a DAO recently raised $47 million in a failed attempt to buy a copy of the constitution.
WHAT TYPE OF WEB3 WILL EMERGE?
With so much up in the air, it’s unclear what type of Web3 will emerge. Although decentralization promises to diminish the power of major corporations, these conglomerates still hold such endless resources that it’s hard to imagine them not finding a way to capitalize and maintain relevance.
Remaking the web won’t happen overnight. There are still major technical and regulatory hurdles which need to be overcome before Web3 becomes the golden standard.
Although we can’t predict how all this will shake out and affect your daily online experience, one thing is for sure—the internet is evolving.