As we detailed last week, the release of iOS 10 marks a major turning point for the software. By opening up internal apps to developers, Apple has offered a major opportunity for businesses to improve and expand the functionality of their apps. Here are a few ways that iOS 10 can help your business.
CISCO INTEGRATION

While Apple announced their partnership with Cisco in August 2015, iOS 10 introduces the fruits of that partnership. Businesses which utilize Cisco networks and iOS devices will see a major improvement in functionality and compatibility. Companies with Cisco networks would be smart to encourage employees to switch to iOS, and companies which use other networks may want to take note of the new changes as they are designed to improve business processes.
OPTIMIZING WIFI
Finding the right AP can make or break major business processes. As a leading network provider, Cisco understands this issue and has used iOS 10 as an opportunity to address it. Devices with iOS 10 recognize Cisco networks, enabling WiFi optimization and prioritization for business critical apps. So if an employee is walking as they take a WebEx meeting on their iPad, rather than scanning all channels for the next strongest signal, Cisco networks use a 801.11k to provide a list of the top six neighboring APs. This saves time and battery. As iPhones reach the end of a cell, they check the location and create a short list of the next best AP based on signal and utilization.
BUSINESS APP PRIORITIZATION
With the bevy of applications, devices and content constantly occupying business networks, network connections can easily become bogged down, slowing business critical processes. Networks typically give apps the same level of priority, regardless of whether they are business apps like voice, messaging, video conferencing and document sharing, or non-business apps like games, movies and social media apps.
Cisco networks allow users to not only configure QoS (Quality of Service) on company infrastructure, but to control the link from client to AP. Thus, even if a wireless network is congested with different app traffic, businesses can “whitelist” critical apps to prioritize them over noncritical apps. IT managers can even whitelist by SSID, allowing them to customize each user profile so that apps are prioritized by what is critical to the individual’s performance. Users can have different settings for different networks, optimizing connections for apps based on whether they are at their office network, school network, home network or somewhere else.
CISCO SPARK INTEGRATION
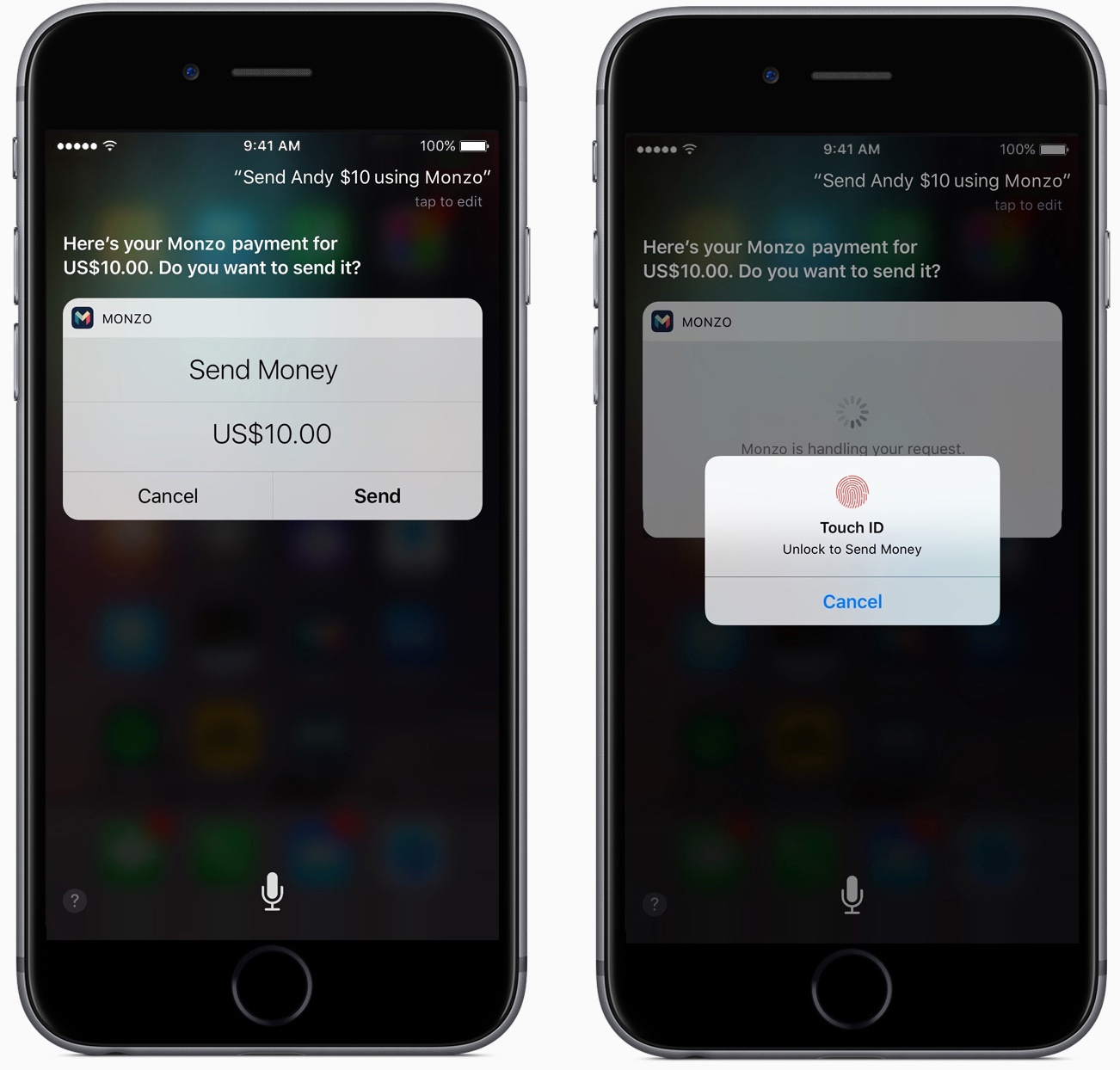
iOS 10 also includes CallKit, a new API which allows VoIP apps like Cisco Spark to be built to take advantage of the accessibility of iOS 10. CallKit enables VoIP apps to utilize the native phone app, ensuring continuity of habit with the native iPhone call experience, while allowing for the superior capabilities of Cisco Spark.
TAKEAWAYS
Cisco’s tests on iOS 10 integrated with Cisco networks have yielded the following results:
- Up to 8 times faster roaming
- 90 percent reduction in web browsing failures
- Up to 66 percent more reliable calling
- Management overhead can be reduced by 50 percent
iMESSAGE FOR BUSINESSES

iMessage has opened its doors to developers, and with it, billions of dollars in market potential. Forbes recently commented: “The launch of the iMessage platform will mint a new generation of billionaire entrepreneurs and become the most valuable social platform in the west over the next five years.”
With a billion active iOS devices worldwide, the iMessage app store has 100 times the distribution footprint compared to the App Store when it launched in 2008. The iMessage store allows for Sticker Packs and iMessage Apps for free or purchase. Aside from creating branding opportunities for celebrities and a whole new platform for social gaming, the iMessage app store opens the door for companies to create extension of their existing apps which utilize iMessage. By integrating internal business apps with internal iOS apps, companies can simplify communication by keeping everything on the same thread.
iOS 10 FOR BUSINESSES
Utilizing the latest software will only improve business processes. iOS 10 provides numerous opportunities for businesses to create more efficient business processes and consolidate business communication on personal devices. It also opens the door for a bevy of future possibilities for businesses to take advantage of as the software evolves. Bring it up at the water cooler and you could change your company for the better.