In the past year, material design has been rising in prominence as both an app and a web design aesthetic. As we’ve detailed in our past article How Material Design Redefined Android App Aesthetics, Material Design has the potential to catch on in a major way. In this post, we take a look at the bright future ahead for the platform.
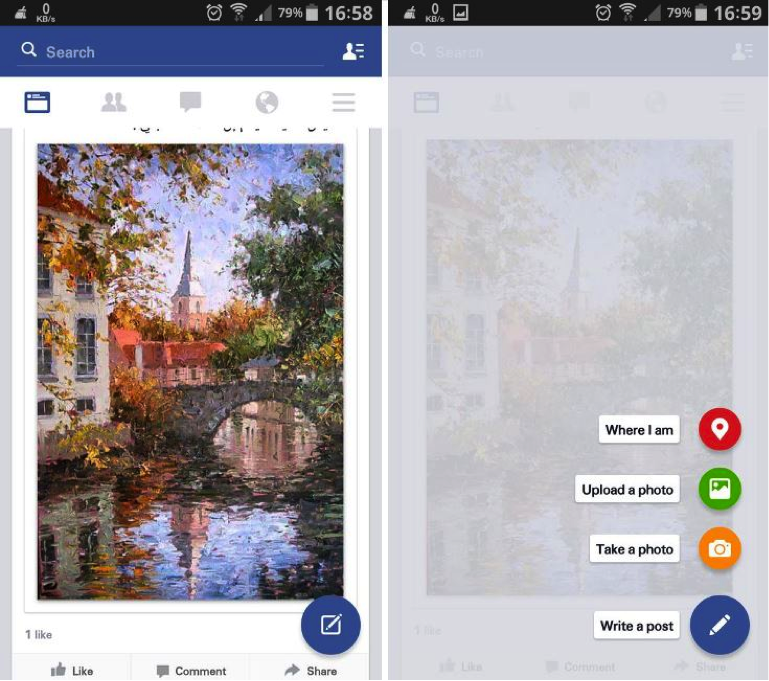
Facebook recently began testing a Material Design overhaul of their Android app. Additions include a floating action button commonly found on Lollipop apps. The design on the whole has a more cohesive digital world adhering to Material Design principals.
“Not only does the app look better, but it’s also going to make the app easier to use for Lollipop users who are now becoming accustomed to that floating action button.” Writes Killian Bell of Techno Buffalo.
Check out this picture of the Beta app (via Techno Buffalo)
If Facebook’s Material Design app looks slick. If it proves to be functionally efficient, it’s reasonable to assume they could utilize some of the same design techniques to update their iOS app.
Facebook’s Android app redesign is reminiscent of the Gmail Inbox app. Considered one of the premier Material Design apps on the market, Inbox was developed by Google and provides a perfect showcase for Material Design aesthetics. Depth plays a major role in all the gestures. When the user swipes an email to mark it done, it reveals a green checkmark underneath the top layer as the email disappears off screen.
Check out his awesome promo video by Google which explains how Inbox works:
Inbox was created to manage mass volumes of emails. Larry Dignan over at ZDNet reviewed Inbox by forwarding his 700 or so work emails per day to the app to see how it handled organizing bulk emails. Inbox passed the test, allowing the user to create bundles of emails in order to better organize incoming messages.
With futurists predicting the downfall of email, the question becomes: Could the same Material Design techniques which the Inbox app uses to organize bulk emails and save screen space be applied to an encompassing Facebook social feed which replaces email?
The main problem inhibiting Material Design from catching on in a major way for the Android platform is device fragmentation. As of March, only 3.3% of Android devices are running the latest OS: Lollipop. 40% of Android devices are running KitKat and 20% are still using Jelly Bean.
Despite the obstacle of device fragmentation, as the next Android OS is released, Lollipop and Material Design are sure to become more and more prevalent. What makes Material Design so crucial is its role in connecting the Android device ecosystem. With more and more devices coming into the fray, Apple has been doing their part to push for Device Continuity, allowing for seamless transition between devices. Android may have to battle to overcome device fragmentation, but as Material Design gains momentum, their hardware and software will at least have aesthetic continuity.
The future of Material Design extends beyond the smartphone and the tablet. With the wearable revolution impending upon Apple Watch’s April 24th release date, it’s reasonable to assume Material Design will find outlets beyond traditional mobile devices as Android increases it’s wearable repertoire. If Google Glass had lasted, no doubt it would have utilized Material Design in its updates. Regardless, Android has several products in the pipeline that are sure to boast Material Design, including Android TV and Android Auto.
For now, Material Design is an Android-exclusive technique still vying for mainstream adoption. However, Facebook’s adoption of the design technique for their upcoming Android app is a good sign. As we look to a device-interconnected world, it seems inevitable the principles of Material Design will continue to evolve and shape the future of Android design aesthetics, and potentially expand to influence web and iOS aesthetics as well.
At Mystic Media, we’re constantly engaged in various app design projects. Our expertise reaches across all facets of the industry, be it iOS design, Android design, web design, strategic marketing and more. Contact us today by clicking here or by phone at 801.994.6815