In the last installment of our blog series on smart cities, we examined how smart infrastructure will revolutionize smart cities. This week, we will examine the many applications which will soon revolutionize smart transportation.
A smarter world means a faster, more efficient and environmentally-friendly world. And perhaps the biggest increase in efficiency and productivity will be driven by the many ways in which AI can optimize the amount of time it takes to get where you’re going.
Here are the top applications in smart transportation coming to a city near you:
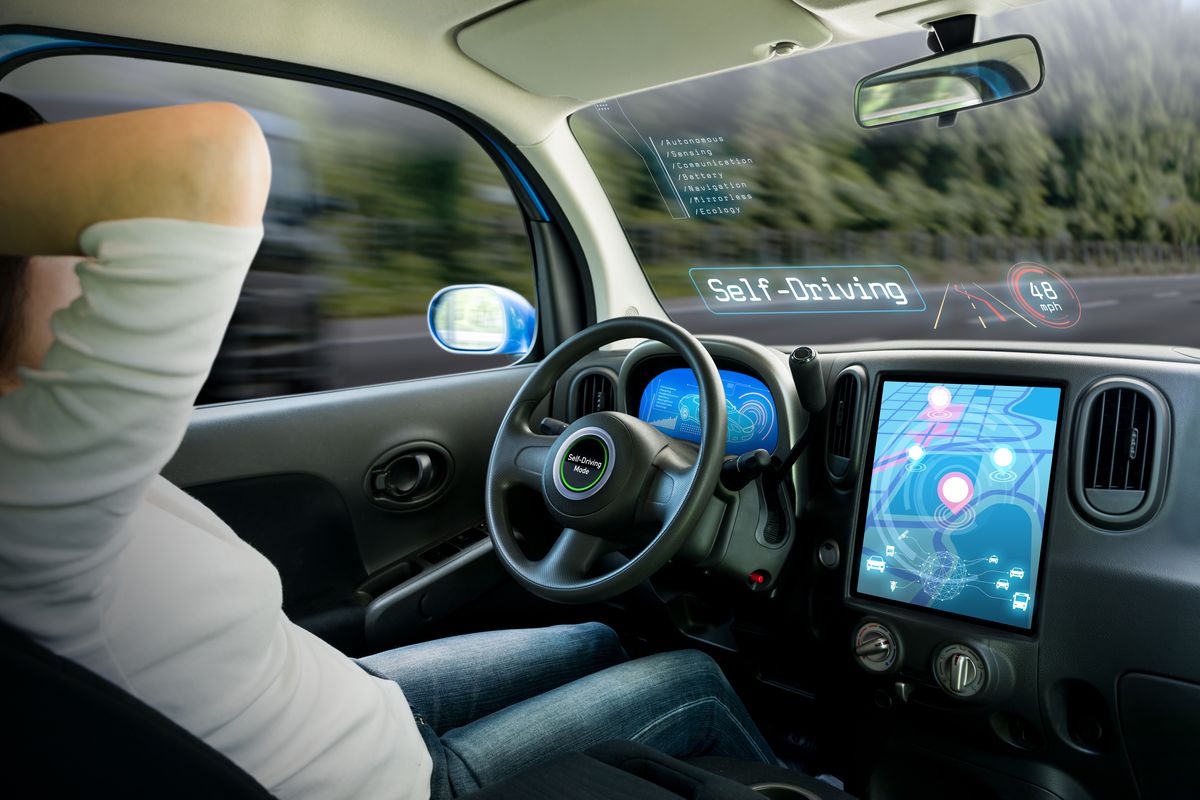
AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES
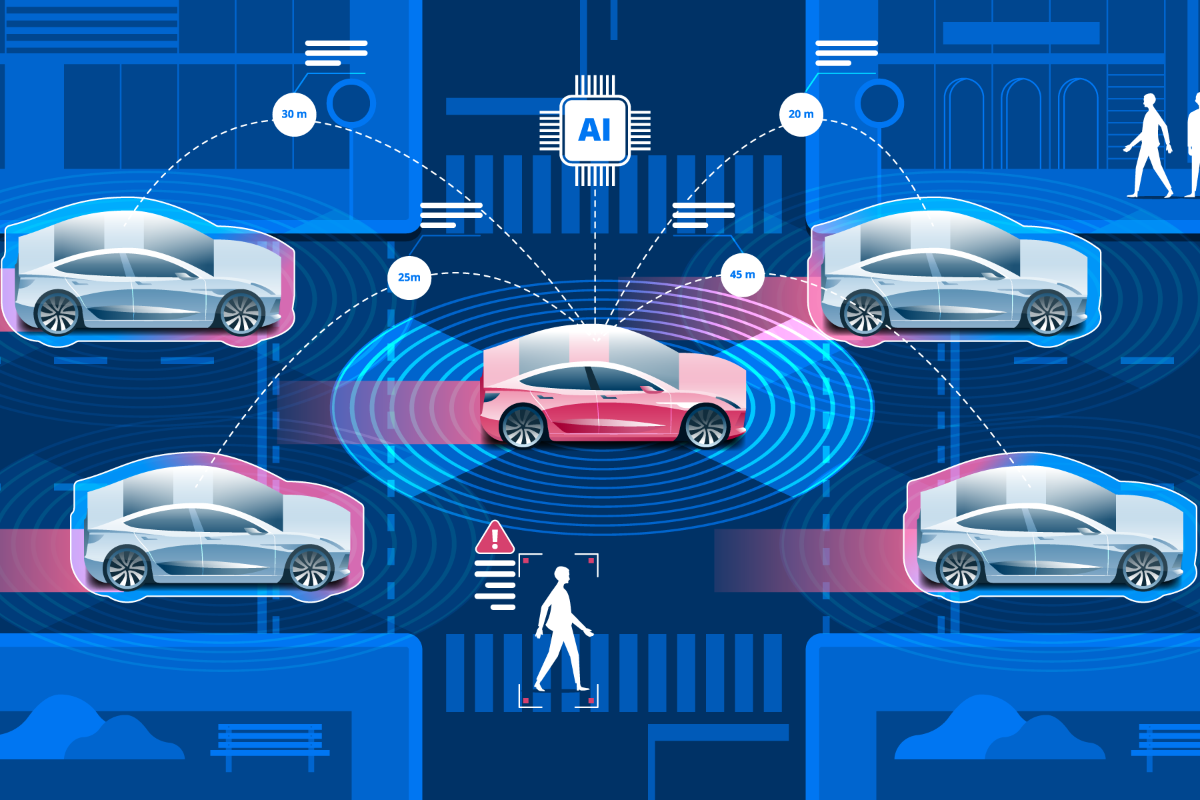
Some say autonomous vehicles are headed to market by 2020. Others say it could take decades before they are on the road. One thing is for certain, they represent a major technological advancement for smart transportation. Autonomous cars will communicate with each other to avoid accidents and contain state-of-the-art sensors to help keep you and your vehicle safe from harm.
Although autonomous vehicles are arguably the largest technological advancement on the horizon, they will also benefit greatly from a variety of smart transportation applications that will accelerate navigating your local metropolis.
SMART ROADS
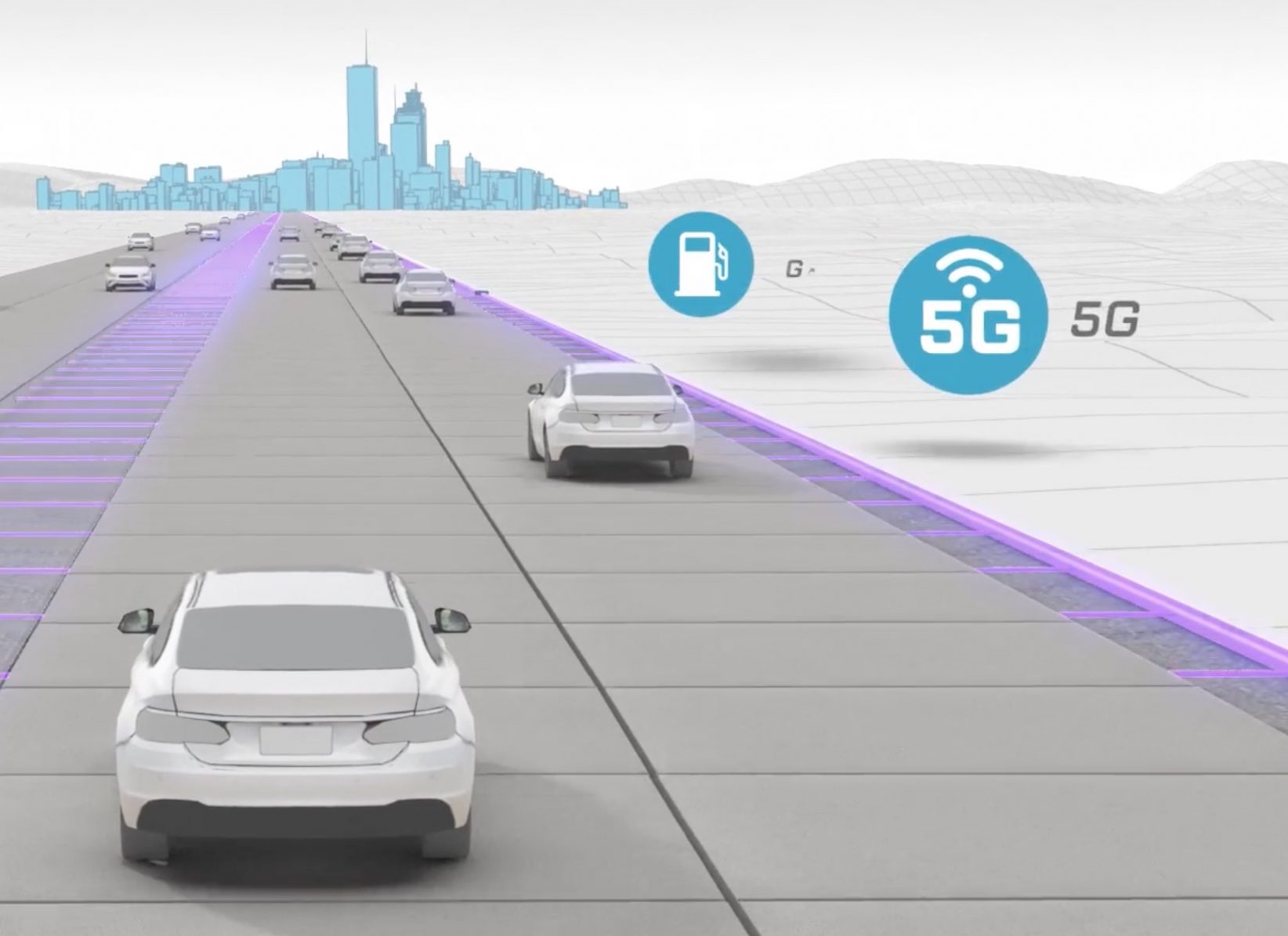
What if we could turn roads into a true digital network, giving real-time traffic updates, supporting autonomous car technology, and providing true connectivity between vehicles and smart cities?
That’s the question tech start-up Integrated Roadways intends to answer. Integrated Roadways develops fiber-connected smart pavement outfitted with a vast amount of sensors, routers, and antennae that send information to data centers along the highway. They recently inked a 5 year deal to test out patented fiber-connected pavement in Colorado.
Smart Roads represent a major advancement in creating vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) connectivity. With 37,133 deaths from motor vehicles on American roads in 2017, the combination of AI applications in smart roads and autonomous cars could revolutionize vehicular transport and create a safer, faster world.
SMART TRAFFIC LIGHTS
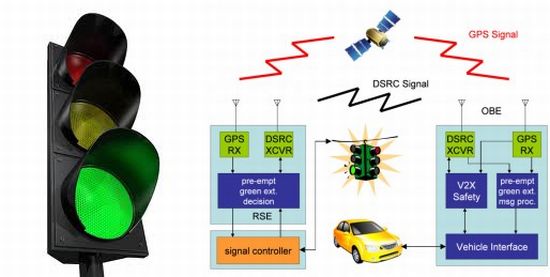
The vehicle-to-infrastructure connectivity spans beyond the roads and into the traffic light. Idling cars generate an estimated 30 million tons of carbon dioxide. Traffic jams can make it harder for first responders to reach emergencies. Rapid Flow proposes that the answer may be their AI-based adaptive traffic management system called Surtrac.
Surtrac uses a decentralized network of smart traffic lights equipped with cameras, radar, and other sensors to manage traffic flows. Surtrac’s sensors identify approaching vehicles, calculate their speed and trajectory, and adjust a traffic signal’s timing schedule as needed.
SMART PUBLIC TRANSIT
There are a variety of smart applications which are revolutionizing public transportation.
In Singapore, hundreds of cameras and sensors citywide analyze traffic congestion and crowd density, enabling government officials to reroute buses at rush hour, reducing the risk of traffic jams. In Indianapolis, the electric Red Line bus service runs a 13 mile path that travels within a quarter of a mile of roughly 150,000 jobs.
One of the major disruptors which has seen rapid adoption in the smart public transport are electric scooter sharing services like Bird and Lime. Electric scooters fill in the public transportation gap for people looking to go 1-3 miles without having to walk or take a taxi. Electric scooters have seen adoption in Los Angeles, San Francisco, Salt Lake City, Brooklyn, and more cities around the globe.
CONCLUSION
Smart cities will have a host of revolutionary applications working in unison and communicating through smart infrastructure with municipalities to ensure maximum efficiency and safety when it comes to transportation. In our next installment of our series on smart cities, we’ll examine how smart security will help keep city-dwellers safe.