In the last installment of our blog series on indoor positioning, we examined an overview of the top indoor positioning technologies. This week, we will examine the most precise and popular method: Bluetooth BLE Beacons and how Bluetooth 5.1 enables them to be the most popular indoor positioning tool on the market.
As the world transitions into a wireless society, Bluetooth technology has evolved and gained more and more popularity. Apple’s decision to remove 1/8th inch audio ports from their devices, while irksome to many consumers, was a definitive move in the direction of Bluetooth.
The growing market for indoor positioning has incentivized an evolution in the landscape of Bluetooth technology. The first consumer bluetooth device was launched in 1999. This year, the world is forecasted to ship more than 4.5 billion Bluetooth devices worldwide. Behind the scenes, manufacturers are using Bluetooth technology for asset tracking and warehouse management. Bluetooth 5.1 technology, in concert with Bluetooth BLE Beacons, is the most popular indoor positioning method.
BLUETOOTH 5.1
Announced in January 2019 by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), Bluetooth 5.1 is the latest and most powerful iteration of Bluetooth technology yet.
Bluetooth 5.1 can connect with other devices at a distance of 985 feet, quadruple Bluetooth 4.0. Bluetooth 5.1 improves upon Bluetooth 4.0’s indoor positioning capabilities with Angle of Arrival (AoA) and Angle of Departure (AoD) features. When used for indoor location, Bluetooth 5.1 can provide up to 1-10 centimeters of accuracy with very little lag. At 48MBps, Bluetooth 5.1 is twice as fast as Bluetooth 4.0.
In addition to being faster and more powerful, Bluetooth 5.1 is the continuation of Low Energy LE, consuming less power than previous iterations of Bluetooth.
INDOOR POSITIONING
Bluetooth BLE Beacons are attached to objects, vehicles, devices, etc. and used to track their location. Bluetooth BLE beacons enable Bluetooth devices to communicate with IoT products and other devices. The top suppliers in the beacon space include Kontakt, Blukii, Minew, Gimbal, Estimote, and EM Microelectronic.
AoA and AoD features are at the core of what enhances positioning technologies in Bluetooth 5.1.
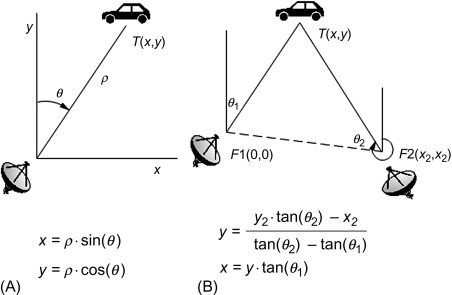
In AoA, the device or tag transmits a specific direction-finding packet using one antenna. The receiving device receives the incoming signal with multiple antennas, each antenna receiving the signal at slightly different times relative to each other. An algorithm factors in the shifts in signal and yields precise coordinate information.
AoD flips the scenario. The device sending the signal has an array of antennas and transmits a packet via the antenna ray. The receiving device then makes an IQ sampling of its antenna to determine the coordinate calculation.
USE CASES
Enhanced indoor positioning enables a number of use cases. In sports stadiums and music venues, a locating hub near the center of the arena can receive signals from devices using AoA technology and determine location coordinates. Keys, perhaps the most commonly lost object, can be embedded with a sensor and located using a locator hub equipped by a smart home.
Bluetooth BLE Beacons, harnessing Bluetooth 5.1, remain the most cost and energy-efficient method of attaining precise indoor positioning locations.
Stay tuned for the next entry in our Indoor Positioning blog series which will explore the wonders of Ultra-Wideband (UWB) technology!


