In 2020, worldwide music streaming revenue hit 11.4 billion dollars, a 2800% growth over the course of a decade. Three hundred forty-one million paid online streaming subscribers get their music from top services like Apple Music, Spotify, and Tidal. The competition for listeners is fierce. Each company looks to leverage every advantage they can in pursuit of higher market share.
Like all major tech conglomerates, music streaming services collect an exceptional amount of user data through their platforms and are creating elaborate AI algorithms designed to improve user experience on a number of levels. Spotify has emerged as the largest on-demand music service active today and bolstered its success through the innovative use of AI.
Here are the top ways in which AI has changed music streaming:
COLLABORATIVE FILTERING
AI has the ability to sift through a plenitude of implicit consumer data, including:
- Song preferences
- Keyword preferences
- Playlist data
- Geographic location of listeners
- Most used devices
AI algorithms can analyze user trends and identify users with similar tastes. For example, if AI deduces that User 1 and User 2 have similar tastes, then it can infer that songs User 1 has liked will also be enjoyed by User 2. Spotify’s algorithms will leverage this information to provide recommendations for User 2 based on what User 1 likes, but User 2 has yet to hear.
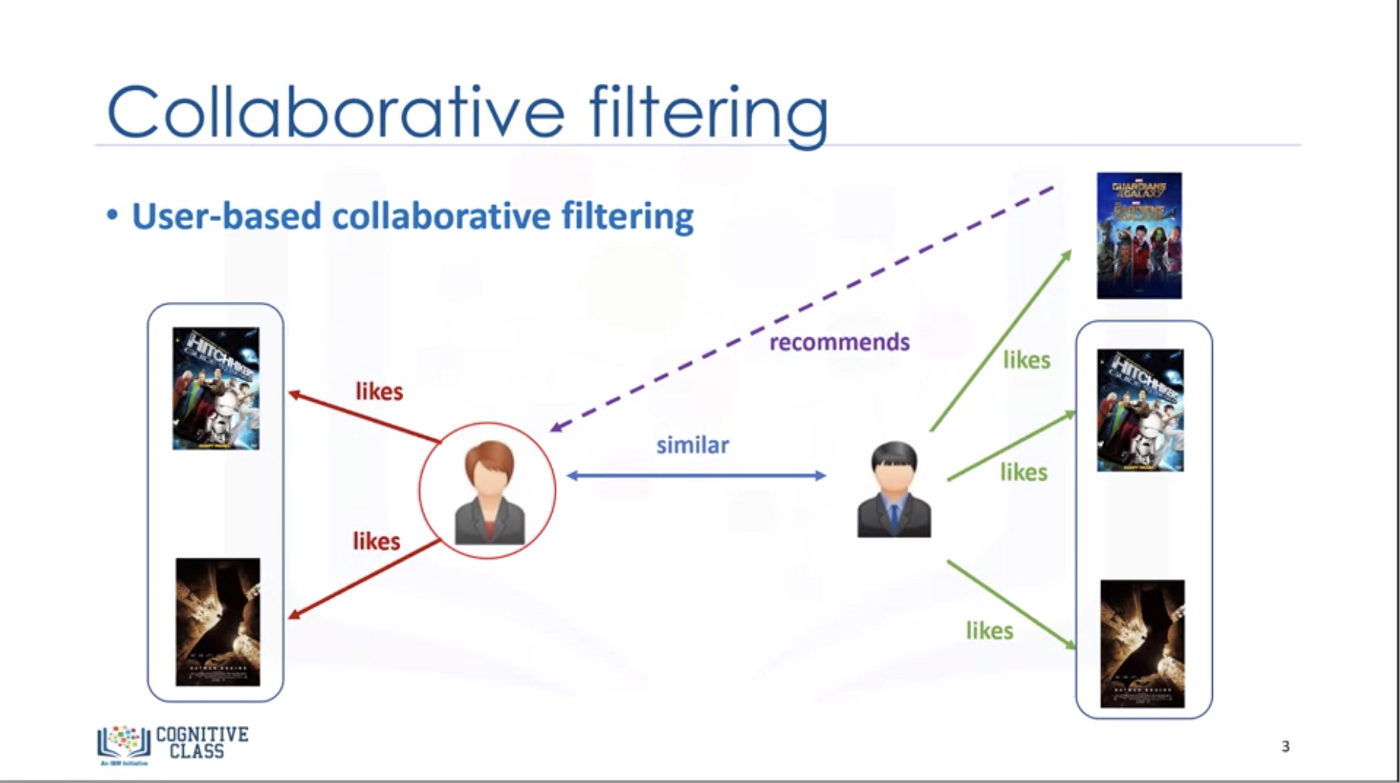
The result is not only improved recommendations, but greater exposure for artists that otherwise may not have been organically found by User 2.
NATURAL LANGUAGE PROCESSING
Natural Language Processing is a burgeoning field in AI. Previously in our blog, we covered GPT-3, the latest Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology developed by OpenAI. Music streaming services are well-versed in the technology and leverage it in a variety of ways to enhance UI.
Algorithms scan a track’s metadata, in addition to blog posts, discussions, and news articles about artists or songs on the internet to determine connections. When artists/songs are mentioned alongside artists/songs the user likes, algorithms make connections that fuel future recommendations.
GPT-3 is not perfect; its ability to track sentiments lacks nuance. As Sonos Radio general manager Ryan Taylor recently said to Fortune Magazine: “The truth is music is entirely subjective… There’s a reason why you listen to Anderson .Paak instead of a song that sounds exactly like Anderson .Paak.”
As NLP technology evolves and algorithms extend their grasp of the nuances of language, so will the recommendations provided to you by music streaming services.
AUDIO MODELS
AI can study audio models to categorize songs exclusively based on their waveforms. This scientific, binary approach to analyzing creative work enables streaming services to categorize songs and create recommendations regardless of the amount of coverage a song or artist has received.
BLOCKCHAIN
Artist payment of royalties on streaming services poses its own challenges, problems, and short-comings. Royalties are deduced from trillions of data points. Luckily, blockchain is helping to facilitate a smoother artist’s payment process. Blockchain technology can not only make the process more transparent but also more efficient. Spotify recently acquired blockchain company Mediachain Labs, which will, many pundits are saying, change royalty payments in streaming forever.
MORE TO COME
While AI has vastly improved streaming ability to keep their subscribers compelled, a long road of evolution lies ahead before it can come to a deep understanding of what motivates our musical tastes and interests. Today’s NLP capabilities provided by GPT-3 will probably become fairly archaic within three years as the technology is pushed further. One thing is clear: as streaming companies amass decades’ worth of user data, they won’t hesitate to leverage it in their pursuit of market dominance.