All well-designed apps begin with an efficient app development process. An inefficient app development process will result in succumbing to pitfalls that will not only prove costly, but also lead to sub-par functionality. Here are our top tips on how to invest wisely in an application development project:
COME PREPARED
When developing your app, you need to know all of the ins and outs of what you want out of your product. During the course of the development process, you will be asked every applicable question and you will need to be able to answer them and to communicate your vision to the app development team so that they are inside your head and know it almost as well as you do.
Rather than waiting for the question to come up, get ahead of it with thorough preparation.
App development starts with the creation of a specifications document elucidating all aspects of the app to be built to ensure a thorough understanding of the idea. Create your own specifications in advance of reaching out to teams and make sure it’s comprehensive. Review the app specifications document thoroughly with prospective partners, make sure they have a comprehensive understanding and it accounts for everything you need your app to do.
Preparation is absolutely vital to staying on the same page with your application development team and avoiding costly hiccups and rebuilds down the line.
FIND THE RIGHT TEAM
Every client has different needs and every app development company has different strengths and weaknesses. Finding the right team is crucial for building the product that will get your business to the next level.
Some clients only need app development specialists, while others look for companies that can take a more holistic approach to their projects and provide input or services on marketing, web development, design and more. Ruminate on your unique needs, research and understand prospective companies strengths and weaknesses, and ensure it is a good match before committing to a long-term partnership with a company.
We recommend seeking a collaborative team with experts in app development as well as project management and the ability to expedite development by putting more programmers on projects. The best app development teams have experienced programmers that have built many apps before and can walk you through the process with ease.
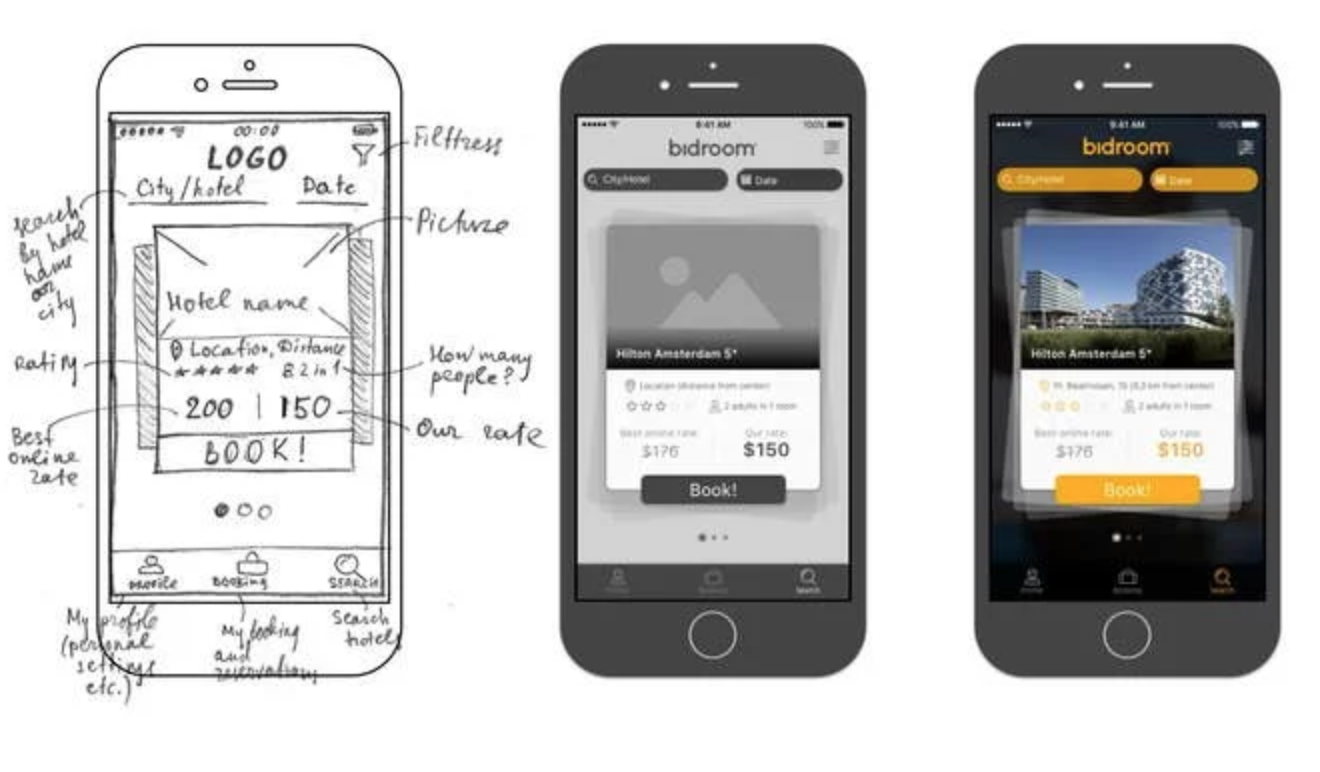
The use of wireframes will save time and money in the app development process. A wireframe is a visual schematic or blueprint that outlines the design for an application without programming the core functions. Mobile app wireframes can take the form of downloadable apps or as websites. Wireframes replicate how the app will work and the flow of screens without incorporating core programming.
Wireframes save time and money because they help app developers get on the same page with their clients without requiring a hefty amount of programming. After reviewing the wireframes, clients can request modifications or approve the designs. The app development team then commences core programming.
The creation of wireframes before programming key functions and additions will save time, money, and headaches.
MAKE IT SCALABLE
Oftentimes when beginning the application development process, businesses elect to start by focusing on the Minimum Viable Product. While understanding what’s needed for the MVP and what’s extraneous to it, it’s vital to have an understanding of what features you may want to add in the future so that the application can be scalable to enable future iterations of the app.
While focusing on Phase 1 of the development process (building the MVP), keep a running wishlist of functions desired for Phase 2 of the development process so that as functions are added and modified, everyone remains cognizant of how current changes will support future functionality.
TEST, TEST, TEST
Testing doesn’t begin upon the completion of the application, it’s an ongoing process that occurs internally as new components of the app are built. It is vital not to underbudget for testing, a common mistake in the app development process.
Core functions need to be repeatedly tested, as does UI and usability. Employing dedicated testers to specialize in testing specific components like core functions, sound, design, and more will ensure a fully-functioning app.
Veteran developers use test-driven development (TDD) in which programmers create tests to define the function or improvements of a function, run tests to see if the test fails, write the code so that tests pass, run tests again, correct the code, and repeat until all tests are passed. Test-driven development guarantees code coverage with unit tests for all functions.
CONCLUSION
When hiring an app development company to build your application, hire for the long haul. An ongoing strategic relationship will help you grow and if you choose the right partner, efficiency will increase as your collaborative relationship develops. A mobile application is a major investment of time and money—invest wisely!
Contact us today to learn about how our team can efficiently build your next mobile app.