Technology has always played an important role in the field of engineering, and the advancements in augmented reality (AR) is no exception. AR enables engineers to visualize and analyze complex designs or models with incredible detail and precision, facilitating their work, and resulting in significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. In this blog post, we will explore how AR is revolutionizing the field of engineering and how it is improving the work of engineering professionals.
SIMPLIFYING COMPLEX MODELS
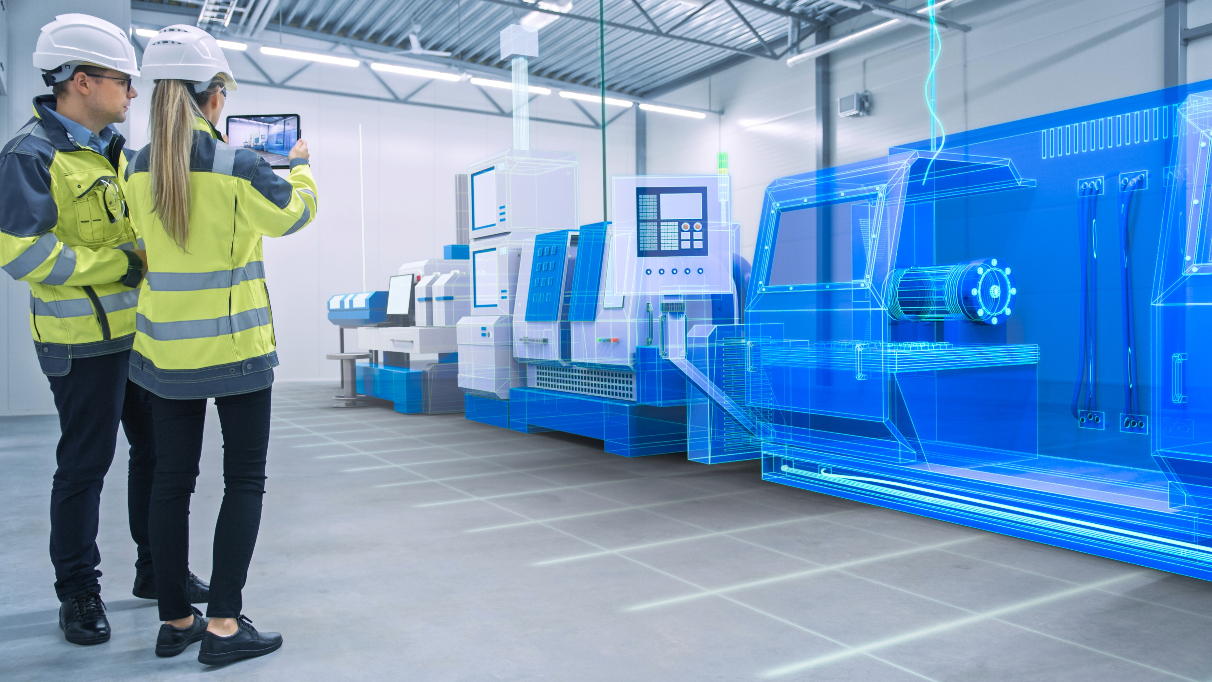

AR helps engineers simplify complex models by superimposing a digital overlay onto the physical world. By doing this, engineers can analyze models in their actual size and scale, making it easier to understand and manipulate for design modifications. AR can aid engineers to identify design flaws much more rapidly with fewer errors.
ENHANCING COLLABORATION
With AR, engineering teams can collaborate more effectively, regardless of their location, utilizing a shared AR model. Multiple team members can view and interact with the same model, which provides better insights and leads to better resolutions.
IMPROVING PRECISION
AR enables engineers to identify and mitigate potential errors before production or assembly. AR headsets can overlay digital design elements in real-time to pinpoint precise positions of mechanical components. As a result, engineering firms can reduce their manufacturing time while increasing the quality of their output.
BOOSTING EFFICIENCY
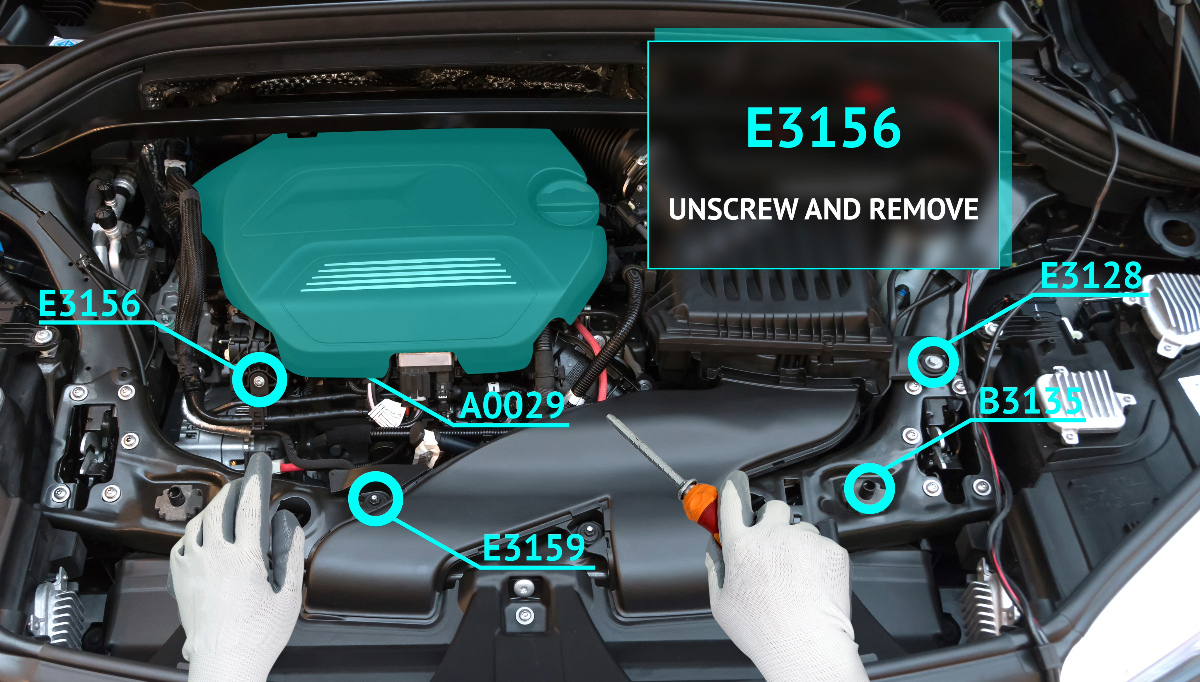
AR helps reduce the time needed for design reviews by allowing engineers to identify optimization opportunities more rapidly. Furthermore, AR can simplify assembly procedures by providing detailed step-by-step guidance through the assembly process, leading to quicker and more accurate builds.
COST REDUCTION
Increased efficiency, improved collaboration, and reduced errors lead to significant cost savings. Applying AR technology to the engineering process is providing substantial cost savings across the industry.
REAL-WORLD EXAMPLES OF AR IN ENGINEERING
AR is not a futuristic concept; it is already being utilized by several leading engineering companies worldwide:
- Boeing: Boeing employs AR glasses for its technicians to aid in assembling complex aircraft. The glasses display instructions and diagrams directly in the technician’s field of view, boosting accuracy and efficiency.
- Volkswagen: Volkswagen has implemented AR technology to assist its assembly line workers. AR headsets provide step-by-step instructions and can highlight specific components and tools needed during the assembly process.
- Siemens: Siemens provides an AR-based maintenance solution for its industrial customers through their “Siemens Industrial Augmented Reality” platform. This technology assists field service technicians in diagnosing and repairing machinery by offering real-time data and guidance.
- Lockheed Martin: Lockheed Martin, a global aerospace and defense company, uses AR to improve the assembly of satellite components. Technicians wearing AR glasses can access digital assembly instructions, reducing errors and accelerating the assembly process.
- Porsche: Porsche employs AR glasses to assist service technicians at their dealerships. These glasses furnish service manuals, schematics, and technical information, allowing technicians to work hands-free.
- Jaguar Land Rover: Jaguar Land Rover utilizes AR in the design and prototyping of vehicles. Engineers can view and manipulate 3D models in a real-world context, easing the evaluation of designs and collaboration on alterations.
- General Electric (GE): GE utilizes AR for equipment maintenance and repair. Technicians can use AR apps on tablets or smart glasses to access digital twins of industrial machines, aiding in diagnostics and maintenance procedures.
- Caterpillar: Caterpillar employs AR technology for training technicians and service personnel. It offers an interactive training module via the “Cat® AR” app for the maintenance and repair of heavy machinery.
- BMW: BMW leverages AR glasses in its production process. These glasses assist workers in assembling and verifying the correct installation of complex components, such as wiring harnesses, by displaying visual instructions and highlighting potential issues.
- Procter & Gamble: This multinational consumer goods corporation uses AR for quality control in its manufacturing processes. It deploys AR systems capable of scanning products for defects, providing real-time feedback to workers.
- ABB: ABB, a global leader in robotics and automation technology, integrates AR into its service and support offerings. AR glasses enable remote experts to aid on-site technicians during maintenance and troubleshooting tasks.
- DHL Supply Chain: DHL has implemented AR smart glasses in its warehouses to improve order picking and inventory management. Warehouse workers receive real-time picking instructions and can scan barcodes with the glasses for accuracy.
As highlighted above, AR is being applied in various ways across the manufacturing industry to enhance productivity, reduce errors, improve training, and streamline operations. AR continues to play a crucial role in transforming manufacturing processes and boosting overall efficiency.
TOP AR TOOLS THAT ARE MAKING WAVES IN THE ENGINEERING WORLD:

The choice of software depends on the specific needs and goals of the engineering project. Here are a few examples:
- AutoCAD AR: AutoCAD, a renowned software for 2D and 3D design, now boasts AR functionality. This allows engineers to visualize their CAD designs in real-world settings, thereby simplifying assessments of how a design will fit into a physical space.
- Trimble Connect: This collaboration platform offers AR capabilities, enabling engineers and construction professionals to overlay 3D models onto real-world job sites, which enhances project planning and management.
- Microsoft HoloLens and Microsoft Mixed Reality: Microsoft’s HoloLens and Mixed Reality platforms provide AR tools for engineers. They allow for viewing and interacting with 3D models, schematics, and data in a mixed reality environment.
- PTC Vuforia: PTC’s Vuforia platform offers AR solutions for industrial applications. It allows engineers to create interactive and immersive AR experiences for tasks like maintenance and training.
- Magic Leap: This company provides spatial computing technology for various applications, including engineering. Engineers can use Magic Leap’s AR headset to interact with 3D models and data in a spatial context.
- EON Reality: EON Reality provides AR and VR solutions for engineering training and education, allowing for the creation of immersive training simulations for various industrial processes.
- SolidWorks XR: SolidWorks, a popular 3D CAD software, offers an extended reality (XR) feature that enables engineers to view and interact with their 3D designs in augmented and virtual reality environments.
- Scope AR WorkLink: This platform provides AR solutions for industrial maintenance and repair. It allows engineers to access step-by-step AR instructions while performing complex maintenance tasks.
- TeamViewer Frontline: This platform, designed for frontline workers, including engineers, offers various AR applications for tasks such as assembly, quality control, and remote assistance. It also allows them to access hands-free information and guidance through smart glasses.
- Fologram: Tailored for architecture, construction, and engineering, Fologram allows engineers to view complex 3D models on job sites and collaborate with colleagues in real time.
These AR software solutions are transforming the way engineers work by enhancing collaboration, improving training and maintenance processes, and providing new ways to visualize and interact with complex data and designs.
TAKEAWAYS
It’s clear that augmented reality has emerged as a powerful tool for the engineering industry. It can simplify tasks, enhance collaboration, improve accuracy, save time and money, and positively impact product quality. By using AR, engineering firms can now optimize their delivery times while simultaneously improving product performance and quality. Engineering professionals that leverage this technology can expect to see significant benefits in their work, ultimately resulting in increased productivity and innovation. It’s no surprise that the engineering industry is now adopting this incredible technology at an ever rapid rate. Augmented reality is more than a trend; it’s a game-changing technology that is here to stay.
In our next blog, we will explore how augmented reality is beneficial to robotics development.

