The Covid-19 pandemic forced lifestyle changes to the global population unlike any other event in recent history. As companies like Amazon and Zoom reap major profits from increased demand for online ordering and teleconferencing, wearable app developers are taking a particular interest in how they can do their part to help quell the pandemic.
It’s easy to take a wearable device that tracks key health metrics and market it as helping to detect Covid-19. It’s much harder to create a device with a proven value in helping prevent the spread of the disease. Here’s our rundown of what you need to know about how wearables can help fight the Covid-19 pandemic.
WEARABLES CANNOT DIAGNOSE COVID-19
In an ideal world, your smartwatch could analyze your body on a molecular level to detect whether you have Covid-19. Technology has not evolved, yet, to where this is possible. The only way to diagnose Covid-19 is through a test administered by a health-care professional.
Fortunately, there are several ways in which wearables can help fight the spread of Covid-19 that do not involve direct diagnosis.
WEARABLES CAN DETECT EARLY SYMPTOMS
Wearables make it easy for their users to monitor general health conditions and deviations from their norms. Although wearables cannot detect the difference between the flu and Covid-19, they can collect data which indicates early symptoms of an illness and warns their users.
Fitbit CEO James Park hopes the device will eventually sense these changes in health data and instruct users to quarantine 1-3 days before symptoms start and to follow-up for confirmation with a coronavirus test.
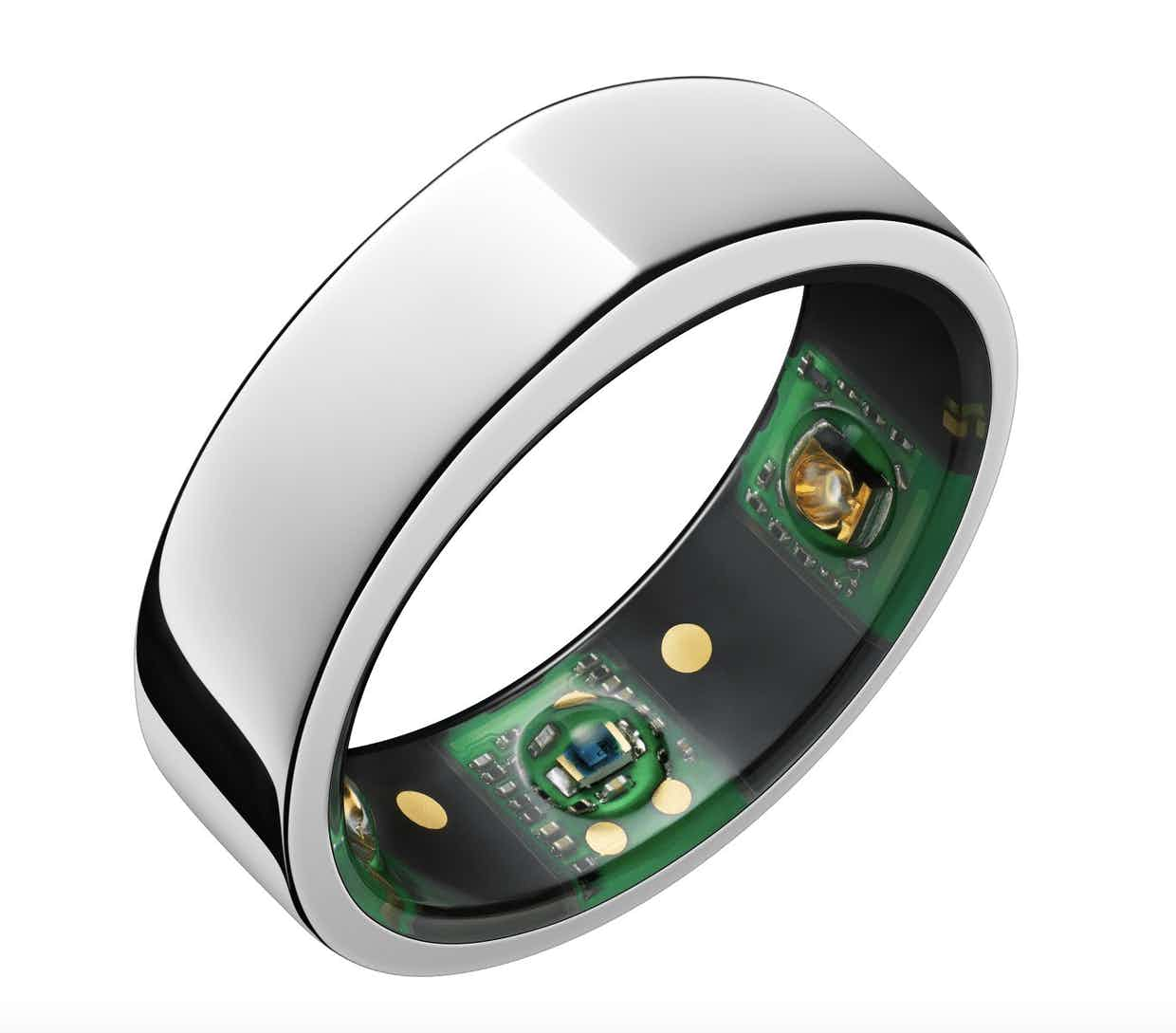

Another big player in the Covid-19 wearables space is the Oura ring. The Oura ring is a smart ring that tracks activity, sleep, temperature, pulse, and heart rate. Since the outbreak, it has emerged as a major tool for detecting early symptoms like increased resting heart rate. Most notably, NBA players in Orlando, Florida use the device to monitor their health and detect early symptoms.
WEARABLES HELP KEEP FRONTLINE HEALTH WORKERS SAFE
John A. Rogers, a biomedical engineer at Northwestern University, has been developing a wearable patch that attaches to the user’s throat and helps monitor coughing and respiratory symptoms like shortness of breath.
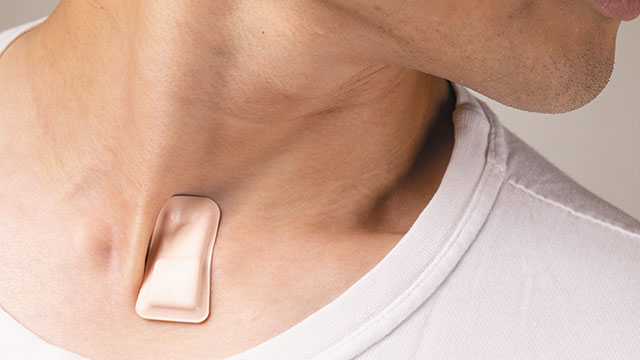
One of the planned uses of this wearable is to protect frontline health-care workers by detecting if they contract the virus and become sick.
In addition, wearables can help monitor symptoms in hospitalized patients. This will reduce the chance of spreading the infection and exposing infected patients to workers.
ASYMPTOMATIC CARRIERS ARE ANOTHER STORY
Although wearables can collect and identify health data that points toward potential infections, recognizing asymptomatic carriers of the Coronavirus is another story. When carriers show no symptoms, the only way to determine if they have been infected is through a test.
TAKEAWAY
Unless there are significant technological leaps in Covid-19 testing, wearables will not be able to detect infections directly. However, they can help catch symptoms early to prevent the spread. Their ability to assist the pandemic represents a major growth sector. We look forward to seeing how wearable developers will innovate to protect the health of users and our future.







